Introduction:
In the modern age of information overload and constant connectivity, the phenomenon of overthinking has become increasingly prevalent. This article delves into the intricacies of overthinking, its detrimental effects on mental well-being, and practical strategies to overcome it.
1. The Spiral of Overthinking:
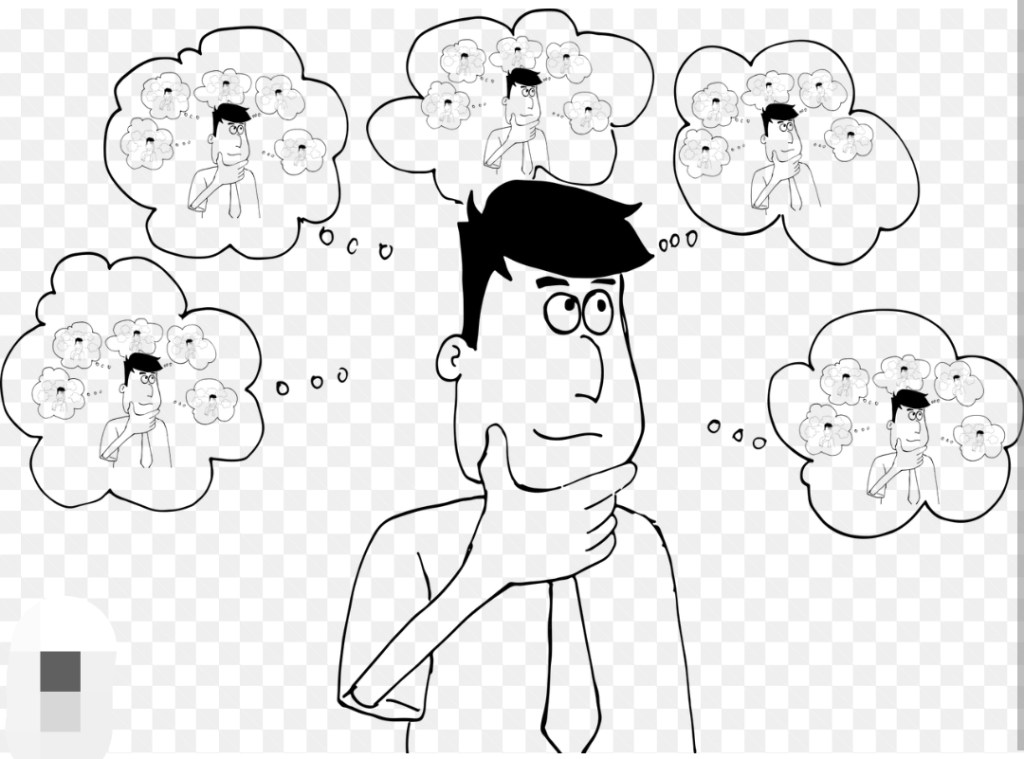
Overthinking is the process of obsessively analyzing and scrutinizing thoughts, situations, or decisions, often leading to a never-ending cycle of doubt and worry. This spiraling thought pattern can hinder decision-making and cause unnecessary stress.
2. The Toll on Mental Health:
Overthinking is not merely a harmless mental exercise; it can take a toll on mental health. Chronic overthinking is associated with increased anxiety, stress, and even depression. Constantly ruminating over past events or anticipating future scenarios can disrupt inner peace.
3. The Illusion of Control:
Overthinkers often fall into the trap of believing that by analyzing every angle of a situation, they can gain a sense of control. However, this illusion of control can lead to paralysis, where decisions are delayed or avoided altogether due to fear of making the wrong choice.
4. Escaping the Overthinking Trap:
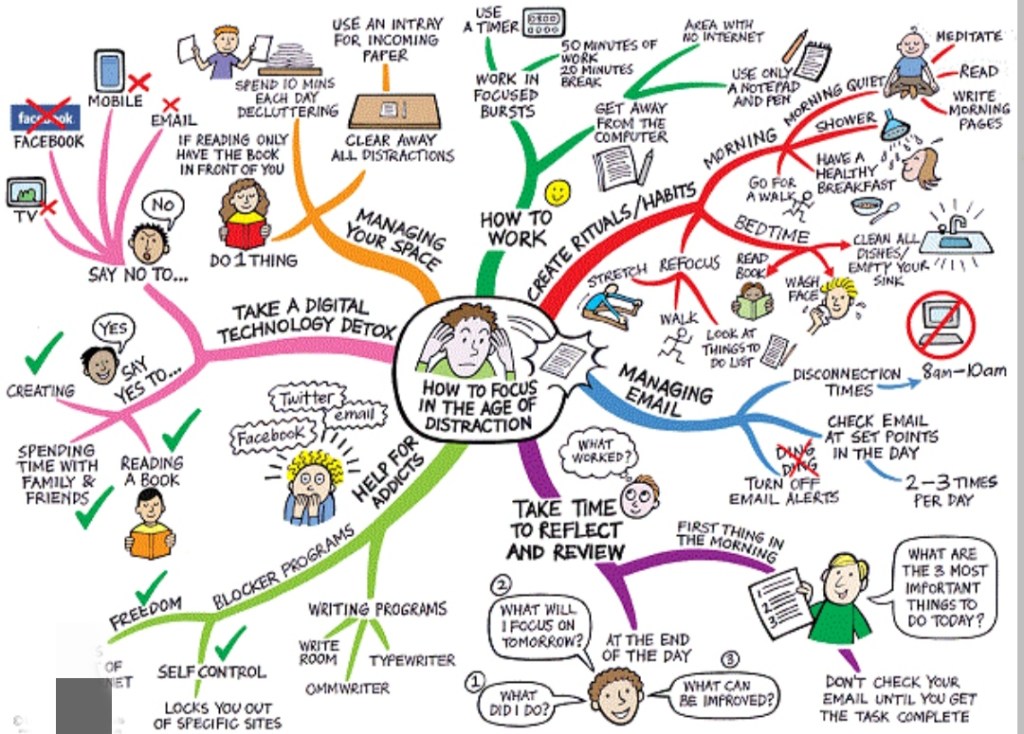
Breaking free from the cycle of overthinking requires conscious effort and mindfulness. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Mindfulness Meditation: Practicing mindfulness meditation helps cultivate awareness of the present moment, allowing overthinkers to distance themselves from intrusive thoughts and regain control over their minds.
- Set Time Limits: Allocate a specific amount of time to think about a particular issue. Once the time is up, make a decision and move forward. This prevents excessive rumination and procrastination.
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: Question the validity of your thoughts. Are they based on facts or assumptions? Challenging negative self-talk can help disrupt the overthinking pattern.
- Engage in Positive Activities: Engaging in activities that bring joy or a sense of accomplishment can redirect your focus away from overthinking and towards positive experiences.
5. Embracing Imperfection:
Perfectionism often fuels overthinking. Embracing the idea that nobody is perfect and that mistakes are a part of growth can alleviate the pressure to constantly analyze and achieve flawlessness.
6. Anzar Showkat, Your Journey to Liberation:
Anzar Showkat, let this article serve as a reminder that overcoming overthinking is a journey worth embarking upon. By applying the strategies discussed here, you can regain control of your thoughts and find freedom from the burdensome weight of constant analysis.
Conclusion:
Overthinking is a universal challenge that many individuals face in today’s fast-paced world. By recognizing the signs, understanding its impacts, and implementing practical strategies, Anzar Showkat, you can break free from the cycle of overthinking. Remember, the power to quiet your mind and embrace a more balanced perspective lies within your grasp.