Introduction:
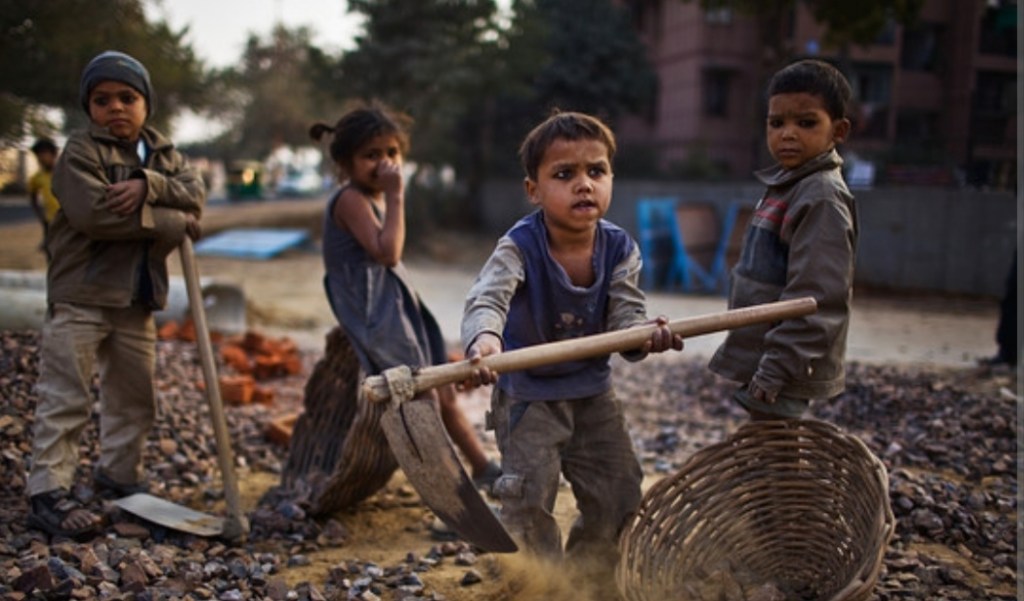
In the heart of many societies, a silent predator lurks, robbing innocent children of their childhood, education, and a promising future. This menacing force is known as child labor, a grave social evil that has persisted across centuries and continents. Despite international efforts to combat it, child labor continues to cast a shadow over the lives of millions of children worldwide. This article sheds light on the alarming reality of child labor, its root causes, consequences, and the urgent need for collective action to eradicate this scourge from our societies.
Root Causes:
Child labor is driven by a complex interplay of socio-economic factors, including poverty, lack of access to quality education, and limited employment opportunities for adults. Families facing financial hardships often feel compelled to send their children to work to supplement their income. Additionally, cultural norms, lack of awareness, and inadequate enforcement of child labor laws contribute to the perpetuation of this practice.
Consequences:
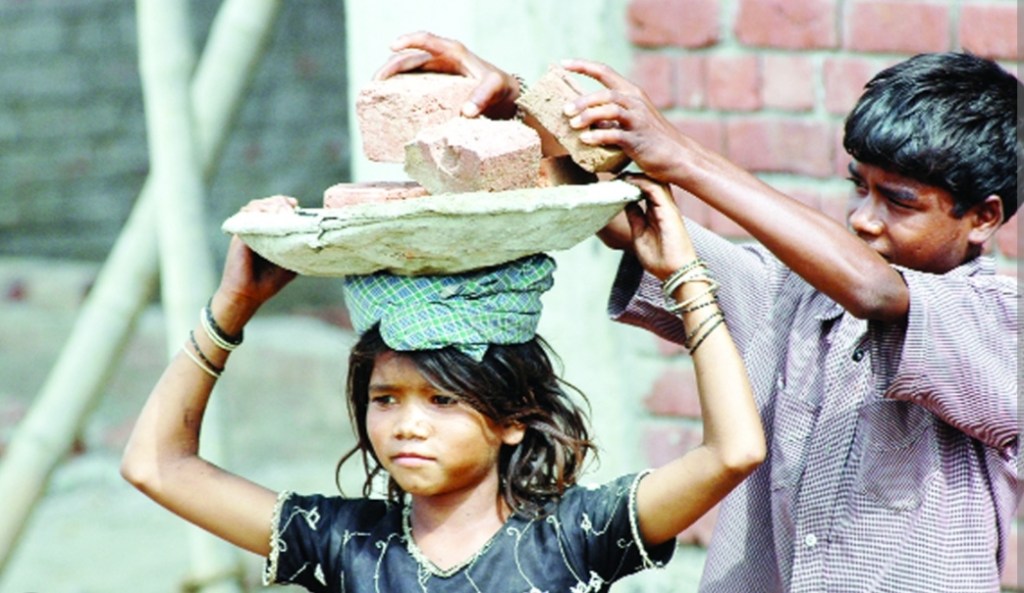
The consequences of child labor are far-reaching and devastating. Children forced into labor are denied their right to education, perpetuating a cycle of illiteracy and poverty. Physical and mental health suffer as well, as these young individuals are subjected to hazardous working conditions, long hours, and minimal rest. The exploitation of children not only robs them of their childhood but also hampers their overall development, limiting their potential to become productive and responsible members of society.
Global Scenario:
Child labor is a global issue that transcends geographical boundaries. It exists in both developing and developed countries, albeit in different forms. From agriculture and manufacturing to domestic work and trafficking, child labor takes on various disguises. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), an estimated 152 million children are engaged in child labor worldwide, with almost half engaged in hazardous work that endangers their safety and well-being.
Combating Child Labor:
Efforts to combat child labor have gained momentum over the years, with international organizations, governments, and civil society working together to address this pressing issue. Key strategies include:
- Strengthening Legislation: Governments must enact and enforce laws that explicitly prohibit child labor, ensuring proper penalties for violators.
- Promoting Education: Investing in quality education and ensuring its accessibility can break the cycle of child labor by offering children better prospects for their future.
- Raising Awareness: Public awareness campaigns can educate communities about the harmful effects of child labor and encourage them to take action against it.
- Supporting Families: Social safety nets, vocational training, and employment opportunities for adults can alleviate the economic pressures that force children into labor.
- Monitoring Supply Chains: Businesses need to ensure that their supply chains are free from child labor and adhere to ethical practices.

Conclusion:
Child labor stands as a glaring testament to the inequities present in our societies. The battle against this social evil is a collective responsibility that requires the dedication of governments, organizations, communities, and individuals alike. Eradicating child labor requires a multifaceted approach that tackles the root causes while fostering an environment where children can flourish, learn, and dream without the shadows of exploitation looming over them. Only through sustained efforts and global solidarity can we hope to eliminate this blight and ensure a brighter future for every child.
By Anzar Showkat